ROLES OF MICROGLIA
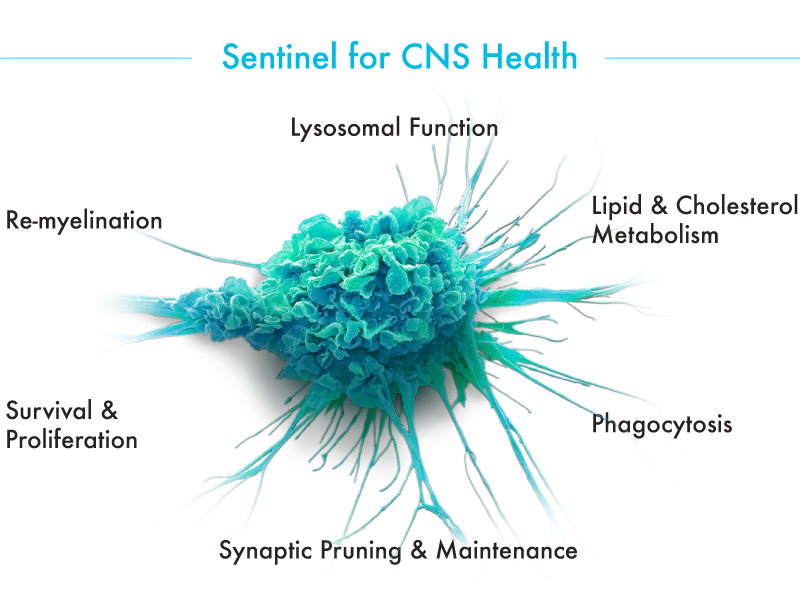
Microglia are the sentinel immune cells of the brain and play a critical role in maintaining CNS health and responding to damage caused by disease
Microglia have several key functions, all of which are important to maintaining normal brain health. They continuously sense and respond to indicators of damage, like infection, cell debris, or plaque buildup that are detected via the TREM2 receptor, which converts microglia into their neuroprotective state.
Our initial focus on microglia and microglia-targeted therapeutics is based on discoveries linking microglial dysfunction to many rare and common neurodegenerative diseases. These conditions include rare, inherited disorders affecting neurons and white matter. Specific examples of these microglia-associated genetic disorders include ALSP, Krabbe, and metachromatic leukodystrophy (MLD). Microglia dysfunction or insufficiency is also linked to increased risk and progression in some of the most common neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s disease (AD), Parkinson’s disease (PD), multiple sclerosis (MS), and Frontotemporal dementia (FTD).